Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
Overview ¶
Package ebiten provides graphics and input API to develop a 2D game.
You can start the game by calling the function RunGame.
// Game implements ebiten.Game interface.
type Game struct{}
// Update proceeds the game state.
// Update is called every tick (1/60 [s] by default).
func (g *Game) Update(screen *ebiten.Image) error {
// Write your game's logical update.
return nil
}
// Draw draws the game screen.
// Draw is called every frame (typically 1/60[s] for 60Hz display).
func (g *Game) Draw(screen *ebiten.Image) {
// Write your game's rendering.
}
// Layout takes the outside size (e.g., the window size) and returns the (logical) screen size.
// If you don't have to adjust the screen size with the outside size, just return a fixed size.
func (g *Game) Layout(outsideWidth, outsideHeight int) (screenWidth, screenHeight int) {
return 320, 240
}
func main() {
game := &Game{}
// Sepcify the window size as you like. Here, a doulbed size is specified.
ebiten.SetWindowSize(640, 480)
ebiten.SetWindowTitle("Your game's title")
// Call ebiten.RunGame to start your game loop.
if err := ebiten.RunGame(game); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
In the API document, 'the main thread' means the goroutine in init(), main() and their callees without 'go' statement. It is assured that 'the main thread' runs on the OS main thread. There are some Ebiten functions that must be called on the main thread under some conditions (typically, before ebiten.RunGame is called).
Environment variables ¶
`EBITEN_SCREENSHOT_KEY` environment variable specifies the key to take a screenshot. For example, if you run your game with `EBITEN_SCREENSHOT_KEY=q`, you can take a game screen's screenshot by pressing Q key. This works only on desktops.
`EBITEN_INTERNAL_IMAGES_KEY` environment variable specifies the key to dump all the internal images. This is valid only when the build tag 'ebitendebug' is specified. This works only on desktops.
Build tags ¶
`ebitendebug` outputs a log of graphics commands. This is useful to know what happens in Ebiten. In general, the number of graphics commands affects the performance of your game.
`ebitengl` forces to use OpenGL in any environments.
Index ¶
- Constants
- Variables
- func CurrentFPS() float64
- func CurrentTPS() float64
- func CursorPosition() (x, y int)
- func DeviceScaleFactor() float64
- func GamepadAxis(id int, axis int) float64
- func GamepadAxisNum(id int) int
- func GamepadButtonNum(id int) int
- func GamepadIDs() []int
- func GamepadName(id int) string
- func GamepadSDLID(id int) string
- func InputChars() []rune
- func IsCursorVisible() booldeprecated
- func IsDrawingSkipped() bool
- func IsFocused() bool
- func IsFullscreen() bool
- func IsGamepadButtonPressed(id int, button GamepadButton) bool
- func IsKeyPressed(key Key) bool
- func IsMouseButtonPressed(mouseButton MouseButton) bool
- func IsRunnableInBackground() booldeprecated
- func IsRunnableOnUnfocused() bool
- func IsRunningSlowly() booldeprecated
- func IsScreenClearedEveryFrame() bool
- func IsScreenTransparent() bool
- func IsVsyncEnabled() bool
- func IsWindowDecorated() bool
- func IsWindowFloating() bool
- func IsWindowMaximized() bool
- func IsWindowMinimized() bool
- func IsWindowResizable() bool
- func MaxTPS() int
- func MaximizeWindow()
- func MinimizeWindow()
- func MonitorSize() (int, int)deprecated
- func RestoreWindow()
- func Run(f func(*Image) error, width, height int, scale float64, title string) errordeprecated
- func RunGame(game Game) error
- func RunGameWithoutMainLoop(game Game)
- func ScreenScale() float64deprecated
- func ScreenSizeInFullscreen() (int, int)
- func SetCursorMode(mode CursorModeType)
- func SetCursorVisibility(visible bool)deprecated
- func SetCursorVisible(visible bool)deprecated
- func SetFullscreen(fullscreen bool)
- func SetInitFocused(focused bool)
- func SetMaxTPS(tps int)
- func SetRunnableInBackground(runnableInBackground bool)deprecated
- func SetRunnableOnUnfocused(runnableOnUnfocused bool)
- func SetScreenClearedEveryFrame(cleared bool)
- func SetScreenScale(scale float64)deprecated
- func SetScreenSize(width, height int)deprecated
- func SetScreenTransparent(transparent bool)
- func SetVsyncEnabled(enabled bool)
- func SetWindowDecorated(decorated bool)
- func SetWindowFloating(float bool)
- func SetWindowIcon(iconImages []image.Image)
- func SetWindowPosition(x, y int)
- func SetWindowResizable(resizable bool)
- func SetWindowSize(width, height int)
- func SetWindowTitle(title string)
- func TouchIDs() []int
- func TouchPosition(id int) (int, int)
- func Wheel() (xoff, yoff float64)
- func WindowPosition() (x, y int)
- func WindowSize() (int, int)
- type Address
- type ColorM
- func Monochrome() ColorMdeprecated
- func RotateHue(theta float64) ColorMdeprecated
- func ScaleColor(r, g, b, a float64) ColorMdeprecated
- func TranslateColor(r, g, b, a float64) ColorMdeprecated
- func (c *ColorM) Add(other ColorM)deprecated
- func (c *ColorM) Apply(clr color.Color) color.Color
- func (c *ColorM) ChangeHSV(hueTheta float64, saturationScale float64, valueScale float64)
- func (c *ColorM) Concat(other ColorM)
- func (c *ColorM) Element(i, j int) float64
- func (c *ColorM) Invert()
- func (c *ColorM) IsInvertible() bool
- func (c *ColorM) Reset()
- func (c *ColorM) RotateHue(theta float64)
- func (c *ColorM) Scale(r, g, b, a float64)
- func (c *ColorM) SetElement(i, j int, element float64)
- func (c *ColorM) String() string
- func (c *ColorM) Translate(r, g, b, a float64)
- type CompositeMode
- type CursorModeType
- type DrawImageOptions
- type DrawRectShaderOptions
- type DrawTrianglesOptions
- type DrawTrianglesShaderOptions
- type Filter
- type Game
- type GamepadButton
- type GeoM
- func RotateGeo(theta float64) GeoMdeprecated
- func ScaleGeo(x, y float64) GeoMdeprecated
- func TranslateGeo(tx, ty float64) GeoMdeprecated
- func (g *GeoM) Add(other GeoM)deprecated
- func (g *GeoM) Apply(x, y float64) (float64, float64)
- func (g *GeoM) Concat(other GeoM)
- func (g *GeoM) Element(i, j int) float64
- func (g *GeoM) Invert()
- func (g *GeoM) IsInvertible() bool
- func (g *GeoM) Reset()
- func (g *GeoM) Rotate(theta float64)
- func (g *GeoM) Scale(x, y float64)
- func (g *GeoM) SetElement(i, j int, element float64)
- func (g *GeoM) Skew(skewX, skewY float64)
- func (g *GeoM) String() string
- func (g *GeoM) Translate(tx, ty float64)
- type Image
- func (i *Image) At(x, y int) color.Color
- func (i *Image) Bounds() image.Rectangle
- func (i *Image) Clear() error
- func (i *Image) ColorModel() color.Model
- func (i *Image) Dispose() error
- func (i *Image) DrawImage(img *Image, options *DrawImageOptions) error
- func (i *Image) DrawRectShader(width, height int, shader *Shader, options *DrawRectShaderOptions)
- func (i *Image) DrawTriangles(vertices []Vertex, indices []uint16, img *Image, options *DrawTrianglesOptions)
- func (i *Image) DrawTrianglesShader(vertices []Vertex, indices []uint16, shader *Shader, ...)
- func (i *Image) Fill(clr color.Color) error
- func (i *Image) ReplacePixels(pixels []byte) error
- func (i *Image) Set(x, y int, clr color.Color)
- func (i *Image) Size() (width, height int)
- func (i *Image) SubImage(r image.Rectangle) image.Image
- type ImagePartdeprecated
- type ImagePartsdeprecated
- type Key
- type MouseButton
- type Shader
- type Touchdeprecated
- func Touches() []Touchdeprecated
- type Vertex
Constants ¶
const ColorMDim = affine.ColorMDim
ColorMDim is a dimension of a ColorM.
const DefaultTPS = 60
DefaultTPS represents a default ticks per second, that represents how many times game updating happens in a second.
const FPS = DefaultTPS
FPS represents the default TPS (tick per second). This is for backward compatibility.
Deprecated: (as of 1.8.0) Use DefaultTPS instead.
const GeoMDim = 3
GeoMDim is a dimension of a GeoM.
const MaxIndicesNum = graphics.IndicesNum
MaxIndicesNum is the maximum number of indices for DrawTriangles.
const UncappedTPS = clock.UncappedTPS
UncappedTPS is a special TPS value that means the game doesn't have limitation on TPS.
Variables ¶
var MaxImageSize = 4096
MaxImageSize represented the maximum size of an image, but now this constant is deprecated.
Deprecated: (as of 1.7.0) No replacement so far.
TODO: Make this replacement (#541)
Functions ¶
func CurrentFPS ¶ added in v1.2.0
func CurrentFPS() float64
CurrentFPS returns the current number of FPS (frames per second), that represents how many swapping buffer happens per second.
On some environments, CurrentFPS doesn't return a reliable value since vsync doesn't work well there. If you want to measure the application's speed, Use CurrentTPS.
CurrentFPS is concurrent-safe.
func CurrentTPS ¶ added in v1.8.0
func CurrentTPS() float64
CurrentTPS returns the current TPS (ticks per second), that represents how many update function is called in a second.
CurrentTPS is concurrent-safe.
func CursorPosition ¶
func CursorPosition() (x, y int)
CursorPosition returns a position of a mouse cursor relative to the game screen (window). The cursor position is 'logical' position and this considers the scale of the screen.
CursorPosition is concurrent-safe.
func DeviceScaleFactor ¶ added in v1.6.0
func DeviceScaleFactor() float64
DeviceScaleFactor returns a device scale factor value of the current monitor which the window belongs to.
DeviceScaleFactor returns a meaningful value on high-DPI display environment, otherwise DeviceScaleFactor returns 1.
DeviceScaleFactor might panic on init function on some devices like Android. Then, it is not recommended to call DeviceScaleFactor from init functions.
DeviceScaleFactor must be called on the main thread before the main loop, and is concurrent-safe after the main loop.
func GamepadAxis ¶ added in v1.2.0
GamepadAxis returns the float value [-1.0 - 1.0] of the given gamepad (id)'s axis (axis).
GamepadAxis is concurrent-safe.
GamepadAxis always returns 0 on iOS.
func GamepadAxisNum ¶ added in v1.2.0
GamepadAxisNum returns the number of axes of the gamepad (id).
GamepadAxisNum is concurrent-safe.
GamepadAxisNum always returns 0 on iOS.
func GamepadButtonNum ¶ added in v1.2.0
GamepadButtonNum returns the number of the buttons of the given gamepad (id).
GamepadButtonNum is concurrent-safe.
GamepadButtonNum always returns 0 on iOS.
func GamepadIDs ¶ added in v1.6.0
func GamepadIDs() []int
GamepadIDs returns a slice indicating available gamepad IDs.
GamepadIDs is concurrent-safe.
GamepadIDs always returns an empty slice on iOS.
func GamepadName ¶ added in v1.11.0
GamepadName returns a string with the name. This function may vary in how it returns descriptions for the same device across platforms for example the following drivers/platforms see a Xbox One controller as the following:
- Windows: "Xbox Controller"
- Chrome: "Xbox 360 Controller (XInput STANDARD GAMEPAD)"
- Firefox: "xinput"
GamepadName always returns an empty string on iOS.
GamepadName is concurrent-safe.
func GamepadSDLID ¶ added in v1.11.0
GamepadSDLID returns a string with the GUID generated in the same way as SDL. To detect devices, see also the community project of gamepad devices database: https://github.com/gabomdq/SDL_GameControllerDB
GamepadSDLID always returns an empty string on browsers and mobiles.
GamepadSDLID is concurrent-safe.
func InputChars ¶ added in v1.6.0
func InputChars() []rune
InputChars return "printable" runes read from the keyboard at the time update is called.
InputChars represents the environment's locale-dependent translation of keyboard input to Unicode characters.
IsKeyPressed is based on a mapping of device (US keyboard) codes to input device keys. "Control" and modifier keys should be handled with IsKeyPressed.
InputChars is concurrent-safe.
On Android (ebitenmobile), EbitenView must be focusable to enable to handle keyboard keys.
Keyboards don't work on iOS yet (#1090).
func IsCursorVisible
deprecated
added in
v1.6.0
func IsCursorVisible() bool
IsCursorVisible reports whether the cursor is visible or not.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0-alpha) Use CursorMode instead.
func IsDrawingSkipped ¶ added in v1.8.0
func IsDrawingSkipped() bool
IsDrawingSkipped returns true if rendering result is not adopted. It is recommended to skip drawing images or screen when IsDrawingSkipped is true.
The typical code with IsDrawingSkipped is this:
func update(screen *ebiten.Image) error {
// Update the state.
// When IsDrawingSkipped is true, the rendered result is not adopted.
// Skip rendering then.
if ebiten.IsDrawingSkipped() {
return nil
}
// Draw something to the screen.
return nil
}
IsDrawingSkipped is useful if you use Run function or RunGame function without implementing Game's Draw. Otherwise, i.e., if you use RunGame function with implementing Game's Draw, IsDrawingSkipped should not be used. If you use RunGame and Draw, IsDrawingSkipped always returns true.
IsDrawingSkipped is concurrent-safe.
func IsFocused ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsFocused() bool
IsFocused returns a boolean value indicating whether the game is in focus or in the foreground.
IsFocused will only return true if IsRunnableOnUnfocused is false.
IsFocused is concurrent-safe.
func IsFullscreen ¶ added in v1.6.0
func IsFullscreen() bool
IsFullscreen reports whether the current mode is fullscreen or not.
IsFullscreen always returns false on browsers. IsFullscreen works as this as of 1.10.0-alpha. Before that, IsFullscreen reported whether the current mode is fullscreen or not.
IsFullscreen always returns false on mobiles.
IsFullscreen is concurrent-safe.
func IsGamepadButtonPressed ¶ added in v1.2.0
func IsGamepadButtonPressed(id int, button GamepadButton) bool
IsGamepadButtonPressed returns the boolean indicating the given button of the gamepad (id) is pressed or not.
If you want to know whether the given button of gamepad (id) started being pressed in the current frame, use inpututil.IsGamepadButtonJustPressed
IsGamepadButtonPressed is concurrent-safe.
The relationships between physical buttons and buttion IDs depend on environments. There can be differences even between Chrome and Firefox.
IsGamepadButtonPressed always returns false on iOS.
func IsKeyPressed ¶
IsKeyPressed returns a boolean indicating whether key is pressed.
If you want to know whether the key started being pressed in the current frame, use inpututil.IsKeyJustPressed
Known issue: On Edge browser, some keys don't work well:
- KeyKPEnter and KeyKPEqual are recognized as KeyEnter and KeyEqual.
- KeyPrintScreen is only treated at keyup event.
IsKeyPressed is concurrent-safe.
On Android (ebitenmobile), EbitenView must be focusable to enable to handle keyboard keys.
Keyboards don't work on iOS yet (#1090).
func IsMouseButtonPressed ¶
func IsMouseButtonPressed(mouseButton MouseButton) bool
IsMouseButtonPressed returns a boolean indicating whether mouseButton is pressed.
If you want to know whether the mouseButton started being pressed in the current frame, use inpututil.IsMouseButtonJustPressed
IsMouseButtonPressed is concurrent-safe.
Note that touch events not longer affect IsMouseButtonPressed's result as of 1.4.0-alpha. Use Touches instead.
func IsRunnableInBackground
deprecated
added in
v1.6.0
func IsRunnableInBackground() bool
IsRunnableInBackground is an old name for IsRunnableOnUnfocused.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0) Use IsRunnableOnUnfocused instead.
func IsRunnableOnUnfocused ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsRunnableOnUnfocused() bool
IsRunnableOnUnfocused returns a boolean value indicating whether the game runs even in background.
IsRunnableOnUnfocused is concurrent-safe.
func IsRunningSlowly
deprecated
added in
v1.3.0
func IsRunningSlowly() bool
IsRunningSlowly is an old name for IsDrawingSkipped.
Deprecated: (as of 1.8.0) Use Game's Draw function instead.
func IsScreenClearedEveryFrame ¶ added in v1.12.0
func IsScreenClearedEveryFrame() bool
IsScreenClearedEveryFrame returns true if the frame isn't cleared at the beginning.
IsScreenClearedEveryFrame is concurrent-safe.
func IsScreenTransparent ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsScreenTransparent() bool
IsScreenTransparent reports whether the window is transparent.
IsScreenTransparent is concurrent-safe.
func IsVsyncEnabled ¶ added in v1.8.0
func IsVsyncEnabled() bool
IsVsyncEnabled returns a boolean value indicating whether the game uses the display's vsync.
IsVsyncEnabled is concurrent-safe.
func IsWindowDecorated ¶ added in v1.7.0
func IsWindowDecorated() bool
IsWindowDecorated reports whether the window is decorated.
IsWindowDecorated is concurrent-safe.
func IsWindowFloating ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsWindowFloating() bool
IsWindowFloating reports whether the window is always shown above all the other windows.
IsWindowFloating returns false on browsers and mobiles.
IsWindowFloating is concurrent-safe.
func IsWindowMaximized ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsWindowMaximized() bool
IsWindowMaximized reports whether the window is maximized or not.
IsWindowMaximized returns false when the window is not resizable.
IsWindowMaximized always returns false on browsers and mobiles.
IsWindowMaximized is concurrent-safe.
func IsWindowMinimized ¶ added in v1.11.0
func IsWindowMinimized() bool
IsWindowMinimized reports whether the window is minimized or not.
IsWindowMinimized always returns false on browsers and mobiles.
IsWindowMinimized is concurrent-safe.
func IsWindowResizable ¶ added in v1.9.0
func IsWindowResizable() bool
IsWindowResizable reports whether the window is resizable by the user's dragging on desktops. On the other environments, IsWindowResizable always returns false.
IsWindowResizable is concurrent-safe.
func MaxTPS ¶ added in v1.8.0
func MaxTPS() int
MaxTPS returns the current maximum TPS.
MaxTPS is concurrent-safe.
func MaximizeWindow ¶ added in v1.11.0
func MaximizeWindow()
MaximizeWindow maximizes the window.
MaximizeWindow panics when the window is not resizable.
MaximizeWindow does nothing on browsers or mobiles.
MaximizeWindow is concurrent-safe.
func MinimizeWindow ¶ added in v1.11.0
func MinimizeWindow()
MinimizeWindow minimizes the window.
If the main loop does not start yet, MinimizeWindow does nothing.
MinimizeWindow does nothing on browsers or mobiles.
MinimizeWindow is concurrent-safe.
func MonitorSize
deprecated
added in
v1.7.0
func RestoreWindow ¶ added in v1.11.0
func RestoreWindow()
RestoreWindow restores the window from its maximized or minimized state.
RestoreWindow panics when the window is not maximized nor minimized.
RestoreWindow is concurrent-safe.
func Run
deprecated
Run starts the main loop and runs the game.
Deprecated: (as of 1.12.0) Use RunGame instead.
f is a function which is called at every frame. The argument (*Image) is the render target that represents the screen. The screen size is based on the given values (width and height).
Run is a shorthand for RunGame, but there are some restrictions. If you want to resize the window by dragging, use RunGame instead.
A window size is based on the given values (width, height and scale).
scale is used to enlarge the screen on desktops. scale is ignored on browsers or mobiles. Note that the actual screen is multiplied not only by the given scale but also by the device scale on high-DPI display. If you pass inverse of the device scale, you can disable this automatical device scaling as a result. You can get the device scale by DeviceScaleFactor function.
On browsers, the scale is automatically adjusted. It is strongly recommended to use iframe if you embed an Ebiten application in your website. scale works as this as of 1.10.0-alpha. Before that, scale affected the rendering scale.
On mobiles, if you use ebitenmobile command, the scale is automatically adjusted.
Run must be called on the main thread. Note that Ebiten bounds the main goroutine to the main OS thread by runtime.LockOSThread.
Ebiten tries to call f 60 times a second by default. In other words, TPS (ticks per second) is 60 by default. This is not related to framerate (display's refresh rate).
f is not called when the window is in background by default. This setting is configurable with SetRunnableOnUnfocused.
The given scale is ignored on fullscreen mode or gomobile-build mode.
On non-GopherJS environments, Run returns error when 1) OpenGL error happens, 2) audio error happens or 3) f returns error. In the case of 3), Run returns the same error.
On GopherJS, Run returns immediately. It is because the 'main' goroutine cannot be blocked on GopherJS due to the bug (gopherjs/gopherjs#826). When an error happens, this is shown as an error on the console.
The size unit is device-independent pixel.
Don't call Run twice or more in one process.
func RunGame ¶ added in v1.11.0
RunGame starts the main loop and runs the game. game's Update function is called every tick to update the game logic. game's Draw function is, if it exists, called every frame to draw the screen. game's Layout function is called when necessary, and you can specify the logical screen size by the function.
game must implement Game interface. Game's Draw function is optional, but it is recommended to implement Draw to seperate updating the logic and rendering.
RunGame is a more flexibile form of Run due to game's Layout function. You can make a resizable window if you use RunGame, while you cannot if you use Run. RunGame is more sophisticated way than Run and hides the notion of 'scale'.
While Run specifies the window size, RunGame does not. You need to call SetWindowSize before RunGame if you want. Otherwise, a default window size is adopted.
Some functions (ScreenScale, SetScreenScale, SetScreenSize) are not available with RunGame.
On browsers, it is strongly recommended to use iframe if you embed an Ebiten application in your website.
RunGame must be called on the main thread. Note that Ebiten bounds the main goroutine to the main OS thread by runtime.LockOSThread.
Ebiten tries to call game's Update function 60 times a second by default. In other words, TPS (ticks per second) is 60 by default. This is not related to framerate (display's refresh rate).
game's Update is not called when the window is in background by default. This setting is configurable with SetRunnableOnUnfocused.
On non-GopherJS environments, RunGame returns error when 1) OpenGL error happens, 2) audio error happens or 3) f returns error. In the case of 3), RunGame returns the same error.
On GopherJS, RunGame returns immediately. It is because the 'main' goroutine cannot be blocked on GopherJS due to the bug (gopherjs/gopherjs#826). When an error happens, this is shown as an error on the console.
The size unit is device-independent pixel.
Don't call RunGame twice or more in one process.
func RunGameWithoutMainLoop ¶ added in v1.11.0
func RunGameWithoutMainLoop(game Game)
RunGameWithoutMainLoop runs the game, but don't call the loop on the main (UI) thread. Different from Run, RunGameWithoutMainLoop returns immediately.
Ebiten users should NOT call RunGameWithoutMainLoop. Instead, functions in github.com/hajimehoshi/ebiten/mobile package calls this.
func ScreenScale
deprecated
added in
v1.3.0
func ScreenScale() float64
ScreenScale returns the game screen scale.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0-alpha) Use WindowSize instead.
func ScreenSizeInFullscreen ¶ added in v1.8.0
ScreenSizeInFullscreen returns the size in device-independent pixels when the game is fullscreen. The adopted monitor is the 'current' monitor which the window belongs to. The returned value can be given to Run or SetSize function if the perfectly fit fullscreen is needed.
On browsers, ScreenSizeInFullscreen returns the 'window' (global object) size, not 'screen' size since an Ebiten game should not know the outside of the window object. For more details, see SetFullscreen API comment.
On mobiles, ScreenSizeInFullscreen returns (0, 0) so far.
ScreenSizeInFullscreen's use cases are limited. If you are making a fullscreen application, you can use RunGame and the Game interface's Layout function instead. If you are making a not-fullscreen application but the application's behavior depends on the monitor size, ScreenSizeInFullscreen is useful.
ScreenSizeInFullscreen must be called on the main thread before ebiten.Run, and is concurrent-safe after ebiten.Run.
func SetCursorMode ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetCursorMode(mode CursorModeType)
SetCursorMode sets the render and capture mode of the mouse cursor. CursorModeVisible sets the cursor to always be visible. CursorModeHidden hides the system cursor when over the window. CursorModeCaptured hides the system cursor and locks it to the window.
On browsers, only CursorModeVisible and CursorModeHidden are supported.
SetCursorMode does nothing on mobiles.
SetCursorMode is concurrent-safe.
func SetCursorVisibility
deprecated
added in
v1.5.0
func SetCursorVisibility(visible bool)
SetCursorVisibility sets the cursor visibility.
Deprecated: (as of 1.6.0-alpha) Use SetCursorMode instead.
func SetCursorVisible
deprecated
added in
v1.6.0
func SetCursorVisible(visible bool)
SetCursorVisible sets the cursor visibility.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0-alpha) Use SetCursorMode instead.
func SetFullscreen ¶ added in v1.6.0
func SetFullscreen(fullscreen bool)
SetFullscreen changes the current mode to fullscreen or not on desktops.
On fullscreen mode, the game screen is automatically enlarged to fit with the monitor. The current scale value is ignored.
On desktops, Ebiten uses 'windowed' fullscreen mode, which doesn't change your monitor's resolution.
SetFullscreen does nothing on browsers. SetFullscreen works as this as of 1.10.0-alpha. Before that, SetFullscreen affected the fullscreen mode.
SetFullscreen does nothing on mobiles.
SetFullscreen does nothing on macOS when the window is fullscreened natively by the macOS desktop instead of SetFullscreen(true).
SetFullscreen is concurrent-safe.
func SetInitFocused ¶ added in v1.12.0
func SetInitFocused(focused bool)
SetInitFocused sets whether the application is focused on show. The default value is true, i.e., the application is focused. Note that the application does not proceed if this is not focused by default. This behavior can be changed by SetRunnableInBackground.
SetInitFocused does nothing on mobile.
SetInitFocused panics if this is called after the main loop.
SetInitFocused is cuncurrent-safe.
func SetMaxTPS ¶ added in v1.8.0
func SetMaxTPS(tps int)
SetMaxTPS sets the maximum TPS (ticks per second), that represents how many updating function is called per second. The initial value is 60.
If tps is UncappedTPS, TPS is uncapped and the game is updated per frame. If tps is negative but not UncappedTPS, SetMaxTPS panics.
SetMaxTPS is concurrent-safe.
func SetRunnableInBackground
deprecated
added in
v1.6.0
func SetRunnableInBackground(runnableInBackground bool)
SetRunnableInBackground is an old name for SetRunnableOnUnfocused.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0-alpha) Use SetRunnableOnUnfocused instead.
func SetRunnableOnUnfocused ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetRunnableOnUnfocused(runnableOnUnfocused bool)
SetRunnableOnUnfocused sets the state if the game runs even in background.
If the given value is true, the game runs in background e.g. when losing focus. The initial state is false.
Known issue: On browsers, even if the state is on, the game doesn't run in background tabs. This is because browsers throttles background tabs not to often update.
SetRunnableOnUnfocused does nothing on mobiles so far.
SetRunnableOnUnfocused is concurrent-safe.
func SetScreenClearedEveryFrame ¶ added in v1.12.0
func SetScreenClearedEveryFrame(cleared bool)
SetScreenClearedEveryFrame enables or disables the clearing of the screen at the beginning of each frame. The default value is true and the screen is cleared each frame by default.
SetScreenClearedEveryFrame is concurrent-safe.
func SetScreenScale
deprecated
added in
v1.2.0
func SetScreenScale(scale float64)
SetScreenScale sets the game screen scale and resizes the window.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0-alpha). Use SetWindowSize instead.
func SetScreenSize
deprecated
added in
v1.2.0
func SetScreenSize(width, height int)
SetScreenSize sets the game screen size and resizes the window.
Deprecated: (as of 1.11.0) Use SetWindowSize and RunGame (Game's Layout) instead.
func SetScreenTransparent ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetScreenTransparent(transparent bool)
SetScreenTransparent sets the state if the window is transparent.
SetScreenTransparent panics if SetScreenTransparent is called after the main loop.
SetScreenTransparent does nothing on mobiles.
SetScreenTransparent is concurrent-safe.
func SetVsyncEnabled ¶ added in v1.8.0
func SetVsyncEnabled(enabled bool)
SetVsyncEnabled sets a boolean value indicating whether the game uses the display's vsync.
If the given value is true, the game tries to sync the display's refresh rate. If false, the game ignores the display's refresh rate. The initial value is true. By disabling vsync, the game works more efficiently but consumes more CPU.
Note that the state doesn't affect TPS (ticks per second, i.e. how many the run function is updated per second).
SetVsyncEnabled does nothing on mobiles so far.
SetVsyncEnabled is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowDecorated ¶ added in v1.7.0
func SetWindowDecorated(decorated bool)
SetWindowDecorated sets the state if the window is decorated.
The window is decorated by default.
SetWindowDecorated works only on desktops. SetWindowDecorated does nothing on other platforms.
SetWindowDecorated does nothing on macOS when the window is fullscreened natively by the macOS desktop instead of SetFullscreen(true).
SetWindowDecorated is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowFloating ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetWindowFloating(float bool)
SetWindowFloating sets the state whether the window is always shown above all the other windows.
SetWindowFloating does nothing on browsers or mobiles.
SetWindowFloating does nothing on macOS when the window is fullscreened natively by the macOS desktop instead of SetFullscreen(true).
SetWindowFloating is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowIcon ¶ added in v1.6.0
SetWindowIcon sets the icon of the game window.
If len(iconImages) is 0, SetWindowIcon reverts the icon to the default one.
For desktops, see the document of glfwSetWindowIcon of GLFW 3.2:
This function sets the icon of the specified window. If passed an array of candidate images, those of or closest to the sizes desired by the system are selected. If no images are specified, the window reverts to its default icon. The desired image sizes varies depending on platform and system settings. The selected images will be rescaled as needed. Good sizes include 16x16, 32x32 and 48x48.
As macOS windows don't have icons, SetWindowIcon doesn't work on macOS.
SetWindowIcon doesn't work on browsers or mobiles.
SetWindowIcon is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowPosition ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetWindowPosition(x, y int)
SetWindowPosition sets the window position. The origin position is the left-upper corner of the current monitor. The unit is device-independent pixels.
SetWindowPosition does nothing on fullscreen mode.
SetWindowPosition does nothing on browsers and mobiles.
SetWindowPosition is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowResizable ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetWindowResizable(resizable bool)
SetWindowResizable sets whether the window is resizable by the user's dragging on desktops. On the other environments, SetWindowResizable does nothing.
The window is not resizable by default.
If SetWindowResizable is called with true and Run is used, SetWindowResizable panics. Use RunGame instead.
SetWindowResizable does nothing on macOS when the window is fullscreened natively by the macOS desktop instead of SetFullscreen(true).
SetWindowResizable is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowSize ¶ added in v1.11.0
func SetWindowSize(width, height int)
SetWindowSize sets the window size on desktops. SetWindowSize does nothing on other environments.
On fullscreen mode, SetWindowSize sets the original window size.
SetWindowSize panics if width or height is not a positive number.
SetWindowSize is concurrent-safe.
func SetWindowTitle ¶ added in v1.7.0
func SetWindowTitle(title string)
SetWindowTitle sets the title of the window.
SetWindowTitle updated the title on browsers, but now does nothing on browsers as of 1.11.0-alpha.
SetWindowTitle does nothing on mobiles.
SetWindowTitle is concurrent-safe.
func TouchIDs ¶ added in v1.7.0
func TouchIDs() []int
TouchIDs returns the current touch states.
If you want to know whether a touch started being pressed in the current frame, use inpututil.JustPressedTouchIDs
TouchIDs returns nil when there are no touches. TouchIDs always returns nil on desktops.
TouchIDs is concurrent-safe.
func TouchPosition ¶ added in v1.7.0
TouchPosition returns the position for the touch of the specified ID.
If the touch of the specified ID is not present, TouchPosition returns (0, 0).
TouchPosition is cuncurrent-safe.
func Wheel ¶ added in v1.8.0
func Wheel() (xoff, yoff float64)
Wheel returns the x and y offset of the mouse wheel or touchpad scroll. It returns 0 if the wheel isn't being rolled.
Wheel is concurrent-safe.
func WindowPosition ¶ added in v1.11.0
func WindowPosition() (x, y int)
WindowPosition returns the window position. The origin position is the left-upper corner of the current monitor. The unit is device-independent pixels.
WindowPosition panics if the main loop does not start yet.
WindowPosition returns the last window position on fullscreen mode.
WindowPosition returns (0, 0) on browsers and mobiles.
WindowPosition is concurrent-safe.
func WindowSize ¶ added in v1.11.0
WindowSize returns the window size on desktops. WindowSize returns (0, 0) on other environments.
On fullscreen mode, WindowSize returns the original window size.
WindowSize is concurrent-safe.
Types ¶
type Address ¶ added in v1.9.0
type Address int
Address represents a sampler address mode.
const ( // AddressClampToZero means that out-of-range texture coordinates return 0 (transparent). AddressClampToZero Address = Address(driver.AddressClampToZero) // AddressRepeat means that texture coordinates wrap to the other side of the texture. AddressRepeat Address = Address(driver.AddressRepeat) // AddressUnsafe means there is no guarantee when the texture coodinates are out of range. AddressUnsafe Address = Address(driver.AddressUnsafe) )
type ColorM ¶
type ColorM struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
A ColorM represents a matrix to transform coloring when rendering an image.
A ColorM is applied to the straight alpha color while an Image's pixels' format is alpha premultiplied. Before applying a matrix, a color is un-multiplied, and after applying the matrix, the color is multiplied again.
The initial value is identity.
func Monochrome
deprecated
func Monochrome() ColorM
Monochrome returns a color matrix for monochrome.
Deprecated: (as of 1.6.0) Use ChangeHSV(0, 0, 1) instead.
func ScaleColor
deprecated
func TranslateColor
deprecated
func (*ColorM) Apply ¶ added in v1.6.0
Apply pre-multiplies a vector (r, g, b, a, 1) by the matrix where r, g, b, and a are clr's values in straight-alpha format. In other words, Apply calculates ColorM * (r, g, b, a, 1)^T.
func (*ColorM) ChangeHSV ¶ added in v1.3.0
ChangeHSV changes HSV (Hue-Saturation-Value) values. hueTheta is a radian value to rotate hue. saturationScale is a value to scale saturation. valueScale is a value to scale value (a.k.a. brightness).
This conversion uses RGB to/from YCrCb conversion.
func (*ColorM) Concat ¶
Concat multiplies a color matrix with the other color matrix. This is same as muptiplying the matrix other and the matrix c in this order.
func (*ColorM) Invert ¶ added in v1.12.0
func (c *ColorM) Invert()
Invert inverts the matrix. If c is not invertible, Invert panics.
func (*ColorM) IsInvertible ¶ added in v1.12.0
IsInvertible returns a boolean value indicating whether the matrix c is invertible or not.
func (*ColorM) Reset ¶ added in v1.5.0
func (c *ColorM) Reset()
Reset resets the ColorM as identity.
func (*ColorM) RotateHue ¶ added in v1.2.0
RotateHue rotates the hue. theta represents rotating angle in radian.
func (*ColorM) SetElement ¶
SetElement sets an element at (i, j).
type CompositeMode ¶ added in v1.3.0
type CompositeMode int
CompositeMode represents Porter-Duff composition mode.
const ( // Regular alpha blending // c_out = c_src + c_dst × (1 - α_src) CompositeModeSourceOver CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeSourceOver) // c_out = 0 CompositeModeClear CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeClear) // c_out = c_src CompositeModeCopy CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeCopy) // c_out = c_dst CompositeModeDestination CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeDestination) // c_out = c_src × (1 - α_dst) + c_dst CompositeModeDestinationOver CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeDestinationOver) // c_out = c_src × α_dst CompositeModeSourceIn CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeSourceIn) // c_out = c_dst × α_src CompositeModeDestinationIn CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeDestinationIn) // c_out = c_src × (1 - α_dst) CompositeModeSourceOut CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeSourceOut) // c_out = c_dst × (1 - α_src) CompositeModeDestinationOut CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeDestinationOut) // c_out = c_src × α_dst + c_dst × (1 - α_src) CompositeModeSourceAtop CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeSourceAtop) // c_out = c_src × (1 - α_dst) + c_dst × α_src CompositeModeDestinationAtop CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeDestinationAtop) // c_out = c_src × (1 - α_dst) + c_dst × (1 - α_src) CompositeModeXor CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeXor) // Sum of source and destination (a.k.a. 'plus' or 'additive') // c_out = c_src + c_dst CompositeModeLighter CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeLighter) // The product of source and destination (a.k.a 'multiply blend mode') // c_out = c_src * c_dst CompositeModeMultiply CompositeMode = CompositeMode(driver.CompositeModeMultiply) )
This name convention follows CSS compositing: https://drafts.fxtf.org/compositing-2/.
In the comments, c_src, c_dst and c_out represent alpha-premultiplied RGB values of source, destination and output respectively. α_src and α_dst represent alpha values of source and destination respectively.
type CursorModeType ¶ added in v1.11.0
type CursorModeType int
CursorModeType represents a render and coordinate mode of a mouse cursor.
const ( CursorModeVisible CursorModeType = CursorModeType(driver.CursorModeVisible) CursorModeHidden CursorModeType = CursorModeType(driver.CursorModeHidden) CursorModeCaptured CursorModeType = CursorModeType(driver.CursorModeCaptured) )
func CursorMode ¶ added in v1.11.0
func CursorMode() CursorModeType
CursorMode returns the current cursor mode.
On browsers, only CursorModeVisible and CursorModeHidden are supported.
CursorMode returns CursorModeHidden on mobiles.
CursorMode is concurrent-safe.
type DrawImageOptions ¶
type DrawImageOptions struct {
// GeoM is a geometry matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which draws the image at (0, 0).
GeoM GeoM
// ColorM is a color matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which doesn't change any color.
ColorM ColorM
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Filter is a type of texture filter.
// The default (zero) value is FilterDefault.
//
// Filter can also be specified at NewImage* functions, but
// specifying filter at DrawImageOptions is recommended (as of 1.7.0).
//
// If both Filter specified at NewImage* and DrawImageOptions are FilterDefault,
// FilterNearest is used.
// If either is FilterDefault and the other is not, the latter is used.
// Otherwise, Filter specified at DrawImageOptions is used.
Filter Filter
// Deprecated: (as of 1.5.0) Use SubImage instead.
ImageParts ImageParts
// Deprecated: (as of 1.1.0) Use SubImage instead.
Parts []ImagePart
// Deprecated: (as of 1.9.0) Use SubImage instead.
SourceRect *image.Rectangle
}
DrawImageOptions represents options for DrawImage.
type DrawRectShaderOptions ¶ added in v1.12.0
type DrawRectShaderOptions struct {
// GeoM is a geometry matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which draws the rectangle at (0, 0).
GeoM GeoM
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Uniforms is a set of uniform variables for the shader.
// The keys are the names of the uniform variables.
// The values must be float or []float.
// If the uniform variable type is an array, a vector or a matrix,
// you have to specify linearly flattened values as a slice.
// For example, if the uniform variable type is [4]vec4, the number of the slice values will be 16.
Uniforms map[string]interface{}
// Images is a set of the source images.
// All the image must be the same size with the rectangle.
Images [4]*Image
}
DrawRectShaderOptions represents options for DrawRectShader.
This API is experimental.
type DrawTrianglesOptions ¶ added in v1.8.0
type DrawTrianglesOptions struct {
// ColorM is a color matrix to draw.
// The default (zero) value is identity, which doesn't change any color.
// ColorM is applied before vertex color scale is applied.
//
// If Shader is not nil, ColorM is ignored.
ColorM ColorM
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Filter is a type of texture filter.
// The default (zero) value is FilterDefault.
Filter Filter
// Address is a sampler address mode.
// The default (zero) value is AddressClampToZero.
Address Address
}
DrawTrianglesOptions represents options for DrawTriangles.
type DrawTrianglesShaderOptions ¶ added in v1.12.0
type DrawTrianglesShaderOptions struct {
// CompositeMode is a composite mode to draw.
// The default (zero) value is regular alpha blending.
CompositeMode CompositeMode
// Uniforms is a set of uniform variables for the shader.
// The keys are the names of the uniform variables.
// The values must be float or []float.
// If the uniform variable type is an array, a vector or a matrix,
// you have to specify linearly flattened values as a slice.
// For example, if the uniform variable type is [4]vec4, the number of the slice values will be 16.
Uniforms map[string]interface{}
// Images is a set of the source images.
// All the image must be the same size.
Images [4]*Image
}
DrawTrianglesShaderOptions represents options for DrawTrianglesShader.
This API is experimental.
type Filter ¶
type Filter int
Filter represents the type of texture filter to be used when an image is maginified or minified.
const ( // FilterDefault represents the default filter. FilterDefault Filter = 0 // FilterNearest represents nearest (crisp-edged) filter FilterNearest Filter = Filter(driver.FilterNearest) // FilterLinear represents linear filter FilterLinear Filter = Filter(driver.FilterLinear) )
type Game ¶ added in v1.11.0
type Game interface {
// Update updates a game by one tick. The given argument represents a screen image.
//
// Basically Update updates the game logic. Whether Update also draws the screen or not depends on the
// existence of Draw implementation.
//
// The Draw function's definition is:
//
// Draw(screen *Image)
//
// With Draw (the recommended way), Update updates only the game logic and Draw draws the screen.
// In this case, the argument screen's updated content by Update is not adopted for the actual game screen,
// and the screen's updated content by Draw is adopted instead.
// In the first frame, it is ensured that Update is called at least once before Draw. You can use Update
// to initialize the game state. After the first frame, Update might not be called or might be called once
// or more for one frame. The frequency is determined by the current TPS (tick-per-second).
//
// Without Draw (the legacy way), Update updates the game logic and also draws the screen.
// In this case, the argument screen's updated content by Update is adopted for the actual game screen.
Update(screen *Image) error
// Layout accepts a native outside size in device-independent pixels and returns the game's logical screen
// size.
//
// On desktops, the outside is a window or a monitor (fullscreen mode). On browsers, the outside is a body
// element. On mobiles, the outside is the view's size.
//
// Even though the outside size and the screen size differ, the rendering scale is automatically adjusted to
// fit with the outside.
//
// Layout is called almost every frame.
//
// If Layout returns non-positive numbers, the caller can panic.
//
// You can return a fixed screen size if you don't care, or you can also return a calculated screen size
// adjusted with the given outside size.
Layout(outsideWidth, outsideHeight int) (screenWidth, screenHeight int)
}
Game defines necessary functions for a game.
type GamepadButton ¶ added in v1.2.0
type GamepadButton int
A GamepadButton represents a gamepad button.
const ( GamepadButton0 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton0) GamepadButton1 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton1) GamepadButton2 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton2) GamepadButton3 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton3) GamepadButton4 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton4) GamepadButton5 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton5) GamepadButton6 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton6) GamepadButton7 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton7) GamepadButton8 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton8) GamepadButton9 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton9) GamepadButton10 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton10) GamepadButton11 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton11) GamepadButton12 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton12) GamepadButton13 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton13) GamepadButton14 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton14) GamepadButton15 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton15) GamepadButton16 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton16) GamepadButton17 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton17) GamepadButton18 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton18) GamepadButton19 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton19) GamepadButton20 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton20) GamepadButton21 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton21) GamepadButton22 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton22) GamepadButton23 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton23) GamepadButton24 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton24) GamepadButton25 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton25) GamepadButton26 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton26) GamepadButton27 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton27) GamepadButton28 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton28) GamepadButton29 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton29) GamepadButton30 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton30) GamepadButton31 GamepadButton = GamepadButton(driver.GamepadButton31) GamepadButtonMax GamepadButton = GamepadButton31 )
GamepadButtons
type GeoM ¶
type GeoM struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
A GeoM represents a matrix to transform geometry when rendering an image.
The initial value is identity.
func TranslateGeo
deprecated
func (*GeoM) Apply ¶ added in v1.6.0
Apply pre-multiplies a vector (x, y, 1) by the matrix. In other words, Apply calculates GeoM * (x, y, 1)^T. The return value is x and y values of the result vector.
func (*GeoM) Concat ¶
Concat multiplies a geometry matrix with the other geometry matrix. This is same as muptiplying the matrix other and the matrix g in this order.
func (*GeoM) Invert ¶ added in v1.7.0
func (g *GeoM) Invert()
Invert inverts the matrix. If g is not invertible, Invert panics.
func (*GeoM) IsInvertible ¶ added in v1.7.0
IsInvertible returns a boolean value indicating whether the matrix g is invertible or not.
func (*GeoM) SetElement ¶
SetElement sets an element at (i, j).
type Image ¶
type Image struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Image represents a rectangle set of pixels. The pixel format is alpha-premultiplied RGBA. Image implements image.Image and draw.Image.
Functions of Image never returns error as of 1.5.0, and error values are always nil.
func NewImage ¶
NewImage returns an empty image.
If width or height is less than 1 or more than device-dependent maximum size, NewImage panics.
filter argument is just for backward compatibility. If you are not sure, specify FilterDefault.
Error returned by NewImage is always nil as of 1.5.0.
func NewImageFromImage ¶
NewImageFromImage creates a new image with the given image (source).
If source's width or height is less than 1 or more than device-dependent maximum size, NewImageFromImage panics.
filter argument is just for backward compatibility. If you are not sure, specify FilterDefault.
Error returned by NewImageFromImage is always nil as of 1.5.0.
func (*Image) At ¶
At returns the color of the image at (x, y).
At loads pixels from GPU to system memory if necessary, which means that At can be slow.
At always returns a transparent color if the image is disposed.
Note that an important logic should not rely on values returned by At, since the returned values can include very slight differences between some machines.
At can't be called outside the main loop (ebiten.Run's updating function) starts (as of version 1.4.0).
func (*Image) Clear ¶
Clear resets the pixels of the image into 0.
When the image is disposed, Clear does nothing.
Clear always returns nil as of 1.5.0.
func (*Image) ColorModel ¶
ColorModel returns the color model of the image.
func (*Image) Dispose ¶ added in v1.2.0
Dispose disposes the image data. After disposing, most of image functions do nothing and returns meaningless values.
Calling Dispose is not mandatory. GC automatically collects internal resources that no objects refer to. However, calling Dispose explicitly is helpful if memory usage matters.
When the image is disposed, Dipose does nothing.
Dipose always return nil as of 1.5.0.
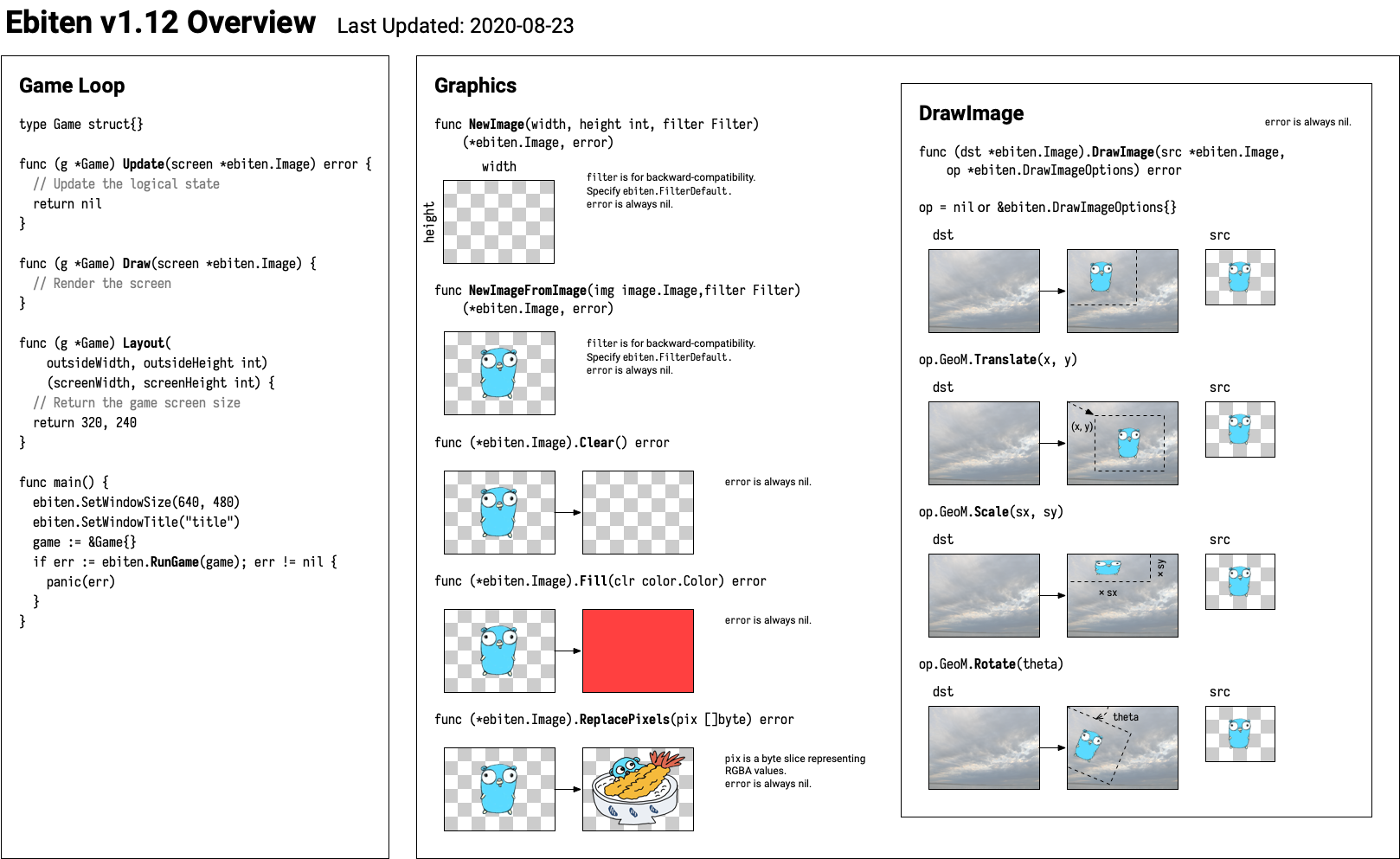
func (*Image) DrawImage ¶
func (i *Image) DrawImage(img *Image, options *DrawImageOptions) error
DrawImage draws the given image on the image i.
DrawImage accepts the options. For details, see the document of DrawImageOptions.
For drawing, the pixels of the argument image at the time of this call is adopted. Even if the argument image is mutated after this call, the drawing result is never affected.
When the image i is disposed, DrawImage does nothing. When the given image img is disposed, DrawImage panics.
When the given image is as same as i, DrawImage panics.
DrawImage works more efficiently as batches when the successive calls of DrawImages satisfy the below conditions:
- All render targets are same (A in A.DrawImage(B, op))
- Either all ColorM element values are same or all the ColorM have only diagonal ('scale') elements
- If only (*ColorM).Scale is applied to a ColorM, the ColorM has only diagonal elements. The other ColorM functions might modify the other elements.
- All CompositeMode values are same
- All Filter values are same
Even when all the above conditions are satisfied, multiple draw commands can be used in really rare cases. Ebiten images usually share an internal automatic texture atlas, but when you consume the atlas, or you create a huge image, those images cannot be on the same texture atlas. In this case, draw commands are separated. The texture atlas size is 4096x4096 so far. Another case is when you use an offscreen as a render source. An offscreen doesn't share the texture atlas with high probability.
For more performance tips, see https://ebiten.org/documents/performancetips.html
DrawImage always returns nil as of 1.5.0.
func (*Image) DrawRectShader ¶ added in v1.12.0
func (i *Image) DrawRectShader(width, height int, shader *Shader, options *DrawRectShaderOptions)
DrawRectShader draws a rectangle with the specified width and height with the specified shader.
For the details about the shader, see https://ebiten.org/documents/shader.html.
When one of the specified image is non-nil and is disposed, DrawRectShader panics.
When the image i is disposed, DrawRectShader does nothing.
This API is experimental.
func (*Image) DrawTriangles ¶ added in v1.8.0
func (i *Image) DrawTriangles(vertices []Vertex, indices []uint16, img *Image, options *DrawTrianglesOptions)
DrawTriangles draws triangles with the specified vertices and their indices.
If len(indices) is not multiple of 3, DrawTriangles panics.
If len(indices) is more than MaxIndicesNum, DrawTriangles panics.
The rule in which DrawTriangles works effectively is same as DrawImage's.
When the given image is disposed, DrawTriangles panics.
When the image i is disposed, DrawTriangles does nothing.
func (*Image) DrawTrianglesShader ¶ added in v1.12.0
func (i *Image) DrawTrianglesShader(vertices []Vertex, indices []uint16, shader *Shader, options *DrawTrianglesShaderOptions)
DrawTrianglesShader draws triangles with the specified vertices and their indices with the specified shader.
For the details about the shader, see https://ebiten.org/documents/shader.html.
If len(indices) is not multiple of 3, DrawTrianglesShader panics.
If len(indices) is more than MaxIndicesNum, DrawTrianglesShader panics.
When a specified image is non-nil and is disposed, DrawTrianglesShader panics.
When the image i is disposed, DrawTrianglesShader does nothing.
This API is experimental.
func (*Image) Fill ¶
Fill fills the image with a solid color.
When the image is disposed, Fill does nothing.
Fill always returns nil as of 1.5.0.
func (*Image) ReplacePixels ¶ added in v1.2.0
ReplacePixels replaces the pixels of the image with p.
The given p must represent RGBA pre-multiplied alpha values. len(pix) must equal to 4 * (bounds width) * (bounds height).
ReplacePixels works on a sub-image.
When len(pix) is not appropriate, ReplacePixels panics.
When the image is disposed, ReplacePixels does nothing.
ReplacePixels always returns nil as of 1.5.0.
func (*Image) Set ¶ added in v1.9.0
Set sets the color at (x, y).
Set loads pixels from GPU to system memory if necessary, which means that Set can be slow.
In the current implementation, successive calls of Set invokes loading pixels at most once, so this is efficient.
If the image is disposed, Set does nothing.
func (*Image) SubImage ¶ added in v1.9.0
SubImage returns an image representing the portion of the image p visible through r. The returned value shares pixels with the original image.
The returned value is always *ebiten.Image.
If the image is disposed, SubImage returns nil.
In the current Ebiten implementation, SubImage is available only as a rendering source.
type Key ¶
type Key int
A Key represents a keyboard key. These keys represent pysical keys of US keyboard. For example, KeyQ represents Q key on US keyboards and ' (quote) key on Dvorak keyboards.
const ( Key0 Key = Key(driver.Key0) Key1 Key = Key(driver.Key1) Key2 Key = Key(driver.Key2) Key3 Key = Key(driver.Key3) Key4 Key = Key(driver.Key4) Key5 Key = Key(driver.Key5) Key6 Key = Key(driver.Key6) Key7 Key = Key(driver.Key7) Key8 Key = Key(driver.Key8) Key9 Key = Key(driver.Key9) KeyA Key = Key(driver.KeyA) KeyB Key = Key(driver.KeyB) KeyC Key = Key(driver.KeyC) KeyD Key = Key(driver.KeyD) KeyE Key = Key(driver.KeyE) KeyF Key = Key(driver.KeyF) KeyG Key = Key(driver.KeyG) KeyH Key = Key(driver.KeyH) KeyI Key = Key(driver.KeyI) KeyJ Key = Key(driver.KeyJ) KeyK Key = Key(driver.KeyK) KeyL Key = Key(driver.KeyL) KeyM Key = Key(driver.KeyM) KeyN Key = Key(driver.KeyN) KeyO Key = Key(driver.KeyO) KeyP Key = Key(driver.KeyP) KeyQ Key = Key(driver.KeyQ) KeyR Key = Key(driver.KeyR) KeyS Key = Key(driver.KeyS) KeyT Key = Key(driver.KeyT) KeyU Key = Key(driver.KeyU) KeyV Key = Key(driver.KeyV) KeyW Key = Key(driver.KeyW) KeyX Key = Key(driver.KeyX) KeyY Key = Key(driver.KeyY) KeyZ Key = Key(driver.KeyZ) KeyApostrophe Key = Key(driver.KeyApostrophe) KeyBackslash Key = Key(driver.KeyBackslash) KeyBackspace Key = Key(driver.KeyBackspace) KeyCapsLock Key = Key(driver.KeyCapsLock) KeyComma Key = Key(driver.KeyComma) KeyDelete Key = Key(driver.KeyDelete) KeyDown Key = Key(driver.KeyDown) KeyEnd Key = Key(driver.KeyEnd) KeyEnter Key = Key(driver.KeyEnter) KeyEqual Key = Key(driver.KeyEqual) KeyEscape Key = Key(driver.KeyEscape) KeyF1 Key = Key(driver.KeyF1) KeyF2 Key = Key(driver.KeyF2) KeyF3 Key = Key(driver.KeyF3) KeyF4 Key = Key(driver.KeyF4) KeyF5 Key = Key(driver.KeyF5) KeyF6 Key = Key(driver.KeyF6) KeyF7 Key = Key(driver.KeyF7) KeyF8 Key = Key(driver.KeyF8) KeyF9 Key = Key(driver.KeyF9) KeyF10 Key = Key(driver.KeyF10) KeyF11 Key = Key(driver.KeyF11) KeyF12 Key = Key(driver.KeyF12) KeyGraveAccent Key = Key(driver.KeyGraveAccent) KeyHome Key = Key(driver.KeyHome) KeyInsert Key = Key(driver.KeyInsert) KeyKP0 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP0) KeyKP1 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP1) KeyKP2 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP2) KeyKP3 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP3) KeyKP4 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP4) KeyKP5 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP5) KeyKP6 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP6) KeyKP7 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP7) KeyKP8 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP8) KeyKP9 Key = Key(driver.KeyKP9) KeyKPAdd Key = Key(driver.KeyKPAdd) KeyKPDecimal Key = Key(driver.KeyKPDecimal) KeyKPDivide Key = Key(driver.KeyKPDivide) KeyKPEnter Key = Key(driver.KeyKPEnter) KeyKPEqual Key = Key(driver.KeyKPEqual) KeyKPMultiply Key = Key(driver.KeyKPMultiply) KeyKPSubtract Key = Key(driver.KeyKPSubtract) KeyLeft Key = Key(driver.KeyLeft) KeyLeftBracket Key = Key(driver.KeyLeftBracket) KeyMenu Key = Key(driver.KeyMenu) KeyMinus Key = Key(driver.KeyMinus) KeyNumLock Key = Key(driver.KeyNumLock) KeyPageDown Key = Key(driver.KeyPageDown) KeyPageUp Key = Key(driver.KeyPageUp) KeyPause Key = Key(driver.KeyPause) KeyPeriod Key = Key(driver.KeyPeriod) KeyPrintScreen Key = Key(driver.KeyPrintScreen) KeyRight Key = Key(driver.KeyRight) KeyRightBracket Key = Key(driver.KeyRightBracket) KeyScrollLock Key = Key(driver.KeyScrollLock) KeySemicolon Key = Key(driver.KeySemicolon) KeySlash Key = Key(driver.KeySlash) KeySpace Key = Key(driver.KeySpace) KeyTab Key = Key(driver.KeyTab) KeyUp Key = Key(driver.KeyUp) KeyAlt Key = Key(driver.KeyReserved0) KeyControl Key = Key(driver.KeyReserved1) KeyShift Key = Key(driver.KeyReserved2) KeyMax Key = KeyShift )
Keys.
type MouseButton ¶
type MouseButton int
A MouseButton represents a mouse button.
const ( MouseButtonLeft MouseButton = MouseButton(driver.MouseButtonLeft) MouseButtonRight MouseButton = MouseButton(driver.MouseButtonRight) MouseButtonMiddle MouseButton = MouseButton(driver.MouseButtonMiddle) )
MouseButtons
type Shader ¶ added in v1.12.0
type Shader struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Shader represents a compiled shader program.
For the details about the shader, see https://ebiten.org/documents/shader.html.
func NewShader ¶ added in v1.12.0
NewShader compiles a shader program in the shading language Kage, and retruns the result.
If the compilation fails, NewShader returns an error.
For the details about the shader, see https://ebiten.org/documents/shader.html.
type Vertex ¶ added in v1.8.0
type Vertex struct {
// DstX and DstY represents a point on a destination image.
DstX float32
DstY float32
// SrcX and SrcY represents a point on a source image.
// Be careful that SrcX/SrcY coordinates are on the image's bounds.
// This means that a left-upper point of a sub-image might not be (0, 0).
SrcX float32
SrcY float32
// ColorR/ColorG/ColorB/ColorA represents color scaling values.
// 1 means the original source image color is used.
// 0 means a transparent color is used.
ColorR float32
ColorG float32
ColorB float32
ColorA float32
}
Vertex represents a vertex passed to DrawTriangles.
 Source Files
¶
Source Files
¶
 Directories
¶
Directories
¶
| Path | Synopsis |
|---|---|
|
Package audio provides audio players.
|
Package audio provides audio players. |
|
mp3
Package mp3 provides MP3 decoder.
|
Package mp3 provides MP3 decoder. |
|
vorbis
Package vorbis provides Ogg/Vorbis decoder.
|
Package vorbis provides Ogg/Vorbis decoder. |
|
wav
Package wav provides WAV (RIFF) decoder.
|
Package wav provides WAV (RIFF) decoder. |
|
cmd
|
|
|
ebitenmobile
ebitenmobile is a wrapper of gomobile for Ebiten.
|
ebitenmobile is a wrapper of gomobile for Ebiten. |
|
Package ebitenutil provides utility functions for Ebiten.
|
Package ebitenutil provides utility functions for Ebiten. |
|
examples
|
|
|
Package inpututil provides utility functions of input like keyboard or mouse.
|
Package inpututil provides utility functions of input like keyboard or mouse. |
|
internal
|
|
|
clock
Package clock manages game timers.
|
Package clock manages game timers. |
|
graphicscommand
Package graphicscommand represents a low layer for graphics using OpenGL.
|
Package graphicscommand represents a low layer for graphics using OpenGL. |
|
graphicsdriver/metal/ca
Package ca provides access to Apple's Core Animation API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/quartzcore).
|
Package ca provides access to Apple's Core Animation API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/quartzcore). |
|
graphicsdriver/metal/mtl
Package mtl provides access to Apple's Metal API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/metal).
|
Package mtl provides access to Apple's Metal API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/metal). |
|
graphicsdriver/metal/ns
Package ns provides access to Apple's AppKit API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/appkit).
|
Package ns provides access to Apple's AppKit API (https://developer.apple.com/documentation/appkit). |
|
graphicsdriver/opengl/gl
Package gl implements Go bindings to OpenGL.
|
Package gl implements Go bindings to OpenGL. |
|
jsutil
Package jsutil offers utility functions for GopherJS and Wasm.
|
Package jsutil offers utility functions for GopherJS and Wasm. |
|
packing
Package packing offers a packing algorithm in 2D space.
|
Package packing offers a packing algorithm in 2D space. |
|
png
Package png implements a PNG image decoder and encoder.
|
Package png implements a PNG image decoder and encoder. |
|
restorable
Package restorable offers an Image struct that stores image commands and restores its pixel data from the commands when context lost happens.
|
Package restorable offers an Image struct that stores image commands and restores its pixel data from the commands when context lost happens. |
|
shaderir
Package shaderir offers intermediate representation for shader programs.
|
Package shaderir offers intermediate representation for shader programs. |
|
testflock
Package testflock provides a lock for testing.
|
Package testflock provides a lock for testing. |
|
Package mobile provides functions for mobile platforms (Android and iOS).
|
Package mobile provides functions for mobile platforms (Android and iOS). |
|
Package text offers functions to draw texts on an Ebiten's image.
|
Package text offers functions to draw texts on an Ebiten's image. |
|
Package vector provides functions for vector graphics rendering.
|
Package vector provides functions for vector graphics rendering. |