< Previous
Next >
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root) Initializes the data structure with the root of the complete binary tree.int insert(int v) Inserts a TreeNode into the tree with value Node.val == val so that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the inserted TreeNode.TreeNode get_root() Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
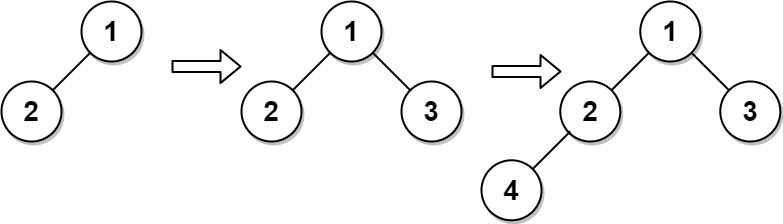
Input
["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"]
[[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []]
Output
[null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]
Explanation
CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]);
cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1
cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2
cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000].
0 <= Node.val <= 5000root is a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104 calls will be made to insert and get_root.
[Tree]
[Breadth-First Search]
[Design]
[Binary Tree]
 Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶