Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
Overview ¶
Package log is a fork of the excellent [`sirupsen/logrus`](https://github.com/bdlm/log) package.
log is a structured logger for Go, completely API compatible with the standard library logger.
Package-level exported logger
package main
import (
"github.com/bdlm/log"
)
func main() {
log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"number": 1,
"size": 10,
}).Info("A walrus appears")
}
Output:
time="2015-09-07T08:48:33Z" level=info msg="A walrus appears" animal=walrus number=1 size=10
API Compatibility ¶
Note that it is completely api-compatible with the stdlib logger, so you can replace your `log` imports everywhere with `"github.com/bdlm/log"` and you'll have the full flexibility of `bdlm/log` available. You can customize it further in your code:
package main
import (
"os"
log "github.com/bdlm/log"
)
func init() {
// Log as JSON instead of the default ASCII formatter.
log.SetFormatter(&log.JSONFormatter{})
// Output to stdout instead of the default stderr. Can be any io.Writer, see
// below for a File example.
log.SetOutput(os.Stdout)
// Only log the warning severity or above.
log.SetLevel(log.WarnLevel)
}
func main() {
log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"size": 10,
}).Info("A group of walrus emerges from the ocean")
log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"omg": true,
"number": 122,
}).Warn("The group's number increased tremendously!")
log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"omg": true,
"number": 100,
}).Fatal("The ice breaks!")
// A common pattern is to re-use fields between logging statements by re-using
// the logrus.Entry returned from WithFields()
contextLogger := log.WithFields(log.Fields{
"common": "this is a common field",
"other": "I also should be logged always",
})
contextLogger.Info("I'll be logged with common and other field")
contextLogger.Info("Me too")
}
Managing secrets ¶
`bdlm/log` also supports a "blacklist" of values that should not be logged. This can be used to help prevent or mitigate leaking secrets into log files:
import (
"github.com/bdlm/log"
)
func main() {
log.AddSecret("some-secret-text")
log.Info("the secret is 'some-secret-text'")
// Output: the secret is '****************'
}
Output to multiple locations ¶
For more advanced usage such as logging to multiple locations from the same application, you can create an instance of the `bdlm/log` Logger:
package main
import (
"os"
"github.com/bdlm/log"
)
// Create a new instance of the logger. You can have any number of instances.
var logger = log.New()
func main() {
// The API for setting attributes is a little different than the package level
// exported logger. See Godoc.
logger.Out = os.Stdout
// You could set this to any `io.Writer` such as a file
// file, err := os.OpenFile("logrus.log", os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
// if err == nil {
// logger.Out = file
// } else {
// logger.Info("Failed to log to file, using default stderr")
// }
logger.WithFields(logrus.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"size": 10,
}).Info("A group of walrus emerges from the ocean")
}
Output features ¶
Color-coded output is available when attached to a TTY for development. A JSON formatter is also available for easy parsing by logstash or Splunk:
log.SetFormatter(&log.JSONFormatter{})
Output:
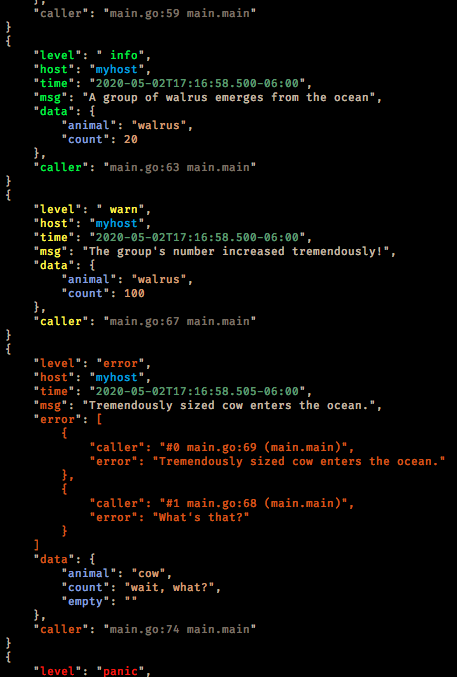
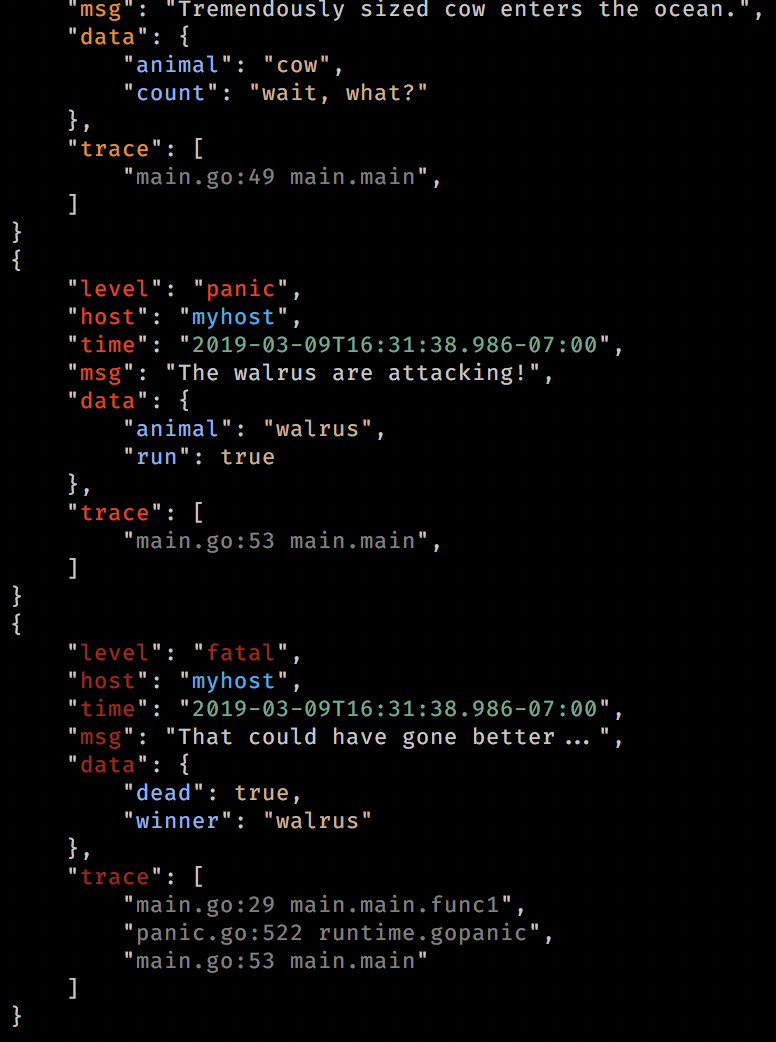
{"caller":"main.go:37 main.main","data":{"animal":"walrus"},"host":"myhost","level":"info","msg":"A group of walrus emerges from the ocean","time":"2018-08-10T23:08:02.860Z"}
{"caller":"main.go:61 main.main","host":"myhost","level":"warning","msg":"The group's number increased tremendously!","number":122,"omg":true,"time":"2018-08-10T23:08:02.863Z"}
{"caller":"main.go:99 main.main","data":{"animal":"walrus"},"host":"myhost","level":"info","msg":"A giant walrus appears!","time":"2018-08-10T23:08:02.877Z"}
{"caller":"main.go:61 main.main","data":{"animal":"walrus","host":"myhost","level":"info","msg":"Tremendously sized cow enters the ocean.","time":"2018-08-10T23:08:02.877Z"}
{"caller":"main.go:99 main.main","host":"myhost","level":"fatal","msg":"The ice breaks!","number":100,"omg":true,"time":"2018-08-10T23:08:03.566Z"}
For a full guide visit https://github.com/bdlm/log
Example (Basic) ¶
package main
import (
"os"
"github.com/bdlm/log"
)
func main() {
var logger = log.New()
logger.Formatter = new(log.TextFormatter) //default
logger.Formatter.(*log.TextFormatter).DisableTimestamp = true // remove timestamp from test output
logger.Formatter.(*log.TextFormatter).DisableHostname = true // remove timestamp from test output
logger.Formatter.(*log.TextFormatter).DisableCaller = true // remove caller from test output
logger.Level = log.DebugLevel
logger.Out = os.Stdout
// Capture the panic result
defer func() {
err := recover()
if err != nil {
entry := err.(*log.Entry)
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"winner": entry.Data["animal"],
"dead": true,
}).Error("That could have gone better...")
}
}()
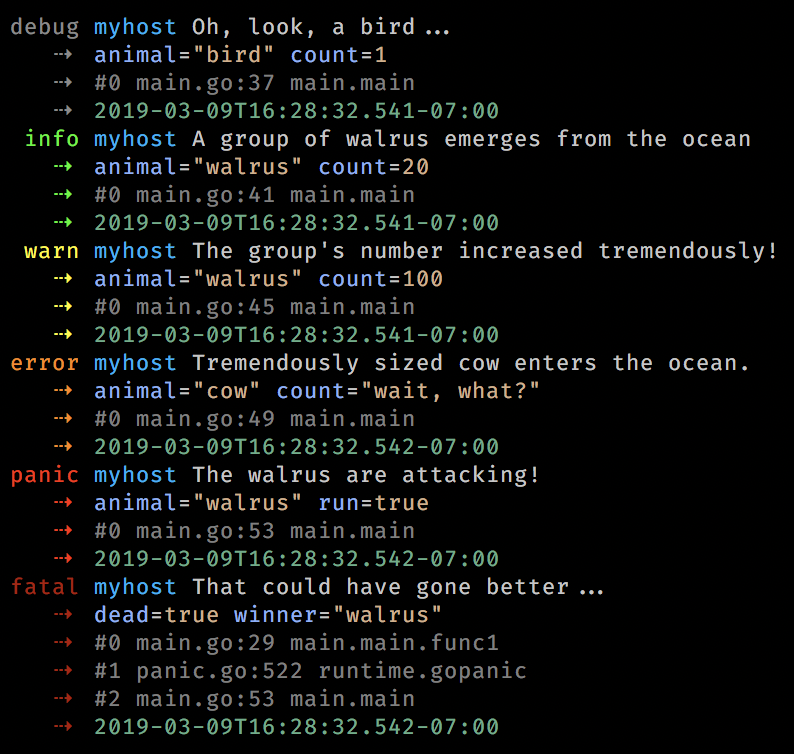
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "bird",
"count": 1,
}).Debug("Oh, look, a bird...")
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"count": 20,
}).Info("A group of walrus emerges from the ocean")
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"count": 100,
}).Warn("The group's number increased tremendously!")
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "cow",
"run": "wait, what?",
}).Error("Tremendously sized cow enters the ocean.")
logger.WithFields(log.Fields{
"animal": "walrus",
"run": true,
}).Panic("The walrus are attacking!")
}
Output: level="debug" msg="Oh, look, a bird..." data.animal="bird" data.count=1 level="info" msg="A group of walrus emerges from the ocean" data.animal="walrus" data.count=20 level="warn" msg="The group's number increased tremendously!" data.animal="walrus" data.count=100 level="error" msg="Tremendously sized cow enters the ocean." data.animal="cow" data.run="wait, what?" level="panic" msg="The walrus are attacking!" data.animal="walrus" data.run=true level="error" msg="That could have gone better..." data.dead=true data.winner="walrus"
Index ¶
- Constants
- Variables
- func AddHook(hook Hook)
- func AddSecret(secret string)
- func Debug(args ...interface{})
- func Debugf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Debugln(args ...interface{})
- func Error(args ...interface{})
- func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Errorln(args ...interface{})
- func Exit(code int)
- func Fatal(args ...interface{})
- func Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Fatalln(args ...interface{})
- func GetLevel() stdLogger.Level
- func Info(args ...interface{})
- func Infof(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Infoln(args ...interface{})
- func LevelString(level stdLogger.Level) string
- func Panic(args ...interface{})
- func Panicf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Panicln(args ...interface{})
- func ParseLevel(lvl string) (stdLogger.Level, error)
- func Print(args ...interface{})
- func Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Println(args ...interface{})
- func RegisterExitHandler(handler func())
- func SetCallerLevel(level int)
- func SetFormatter(formatter Formatter)
- func SetLevel(level stdLogger.Level)
- func SetOutput(out io.Writer)
- func Warn(args ...interface{})
- func Warnf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Warning(args ...interface{})
- func Warningf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func Warningln(args ...interface{})
- func Warnln(args ...interface{})
- type Entry
- func (entry *Entry) Debug(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Debugf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Debugln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Error(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Errorf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Errorln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Fatal(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Fatalln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Info(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Infof(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Infoln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Panic(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Panicf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Panicln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Print(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Println(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) String() (string, error)
- func (entry *Entry) Warn(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Warnf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Warning(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Warningf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Warningln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) Warnln(args ...interface{})
- func (entry *Entry) WithError(err error) *Entry
- func (entry *Entry) WithField(key string, value interface{}) *Entry
- func (entry *Entry) WithFields(fields Fields) *Entry
- func (entry *Entry) WithTime(t time.Time) *Entry
- func (entry *Entry) Writer() *io.PipeWriter
- func (entry *Entry) WriterLevel(level stdLogger.Level) *io.PipeWriter
- type FieldLabel
- type FieldLogger
- type FieldMap
- type Fields
- type Formatter
- type Hook
- type JSONFormatter
- type LevelHooks
- type Logger
- func (logger *Logger) AddHook(hook Hook)
- func (logger *Logger) Debug(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Debugf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Debugln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Error(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Errorf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Errorln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Fatal(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Fatalln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Info(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Infof(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Infoln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Panic(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Panicf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Panicln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Print(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Println(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) SetLevel(level stdLogger.Level)
- func (logger *Logger) SetNoLock()
- func (logger *Logger) SetOutput(out io.Writer)
- func (logger *Logger) Warn(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Warnf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Warning(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Warningf(format string, args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Warningln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) Warnln(args ...interface{})
- func (logger *Logger) WithError(err error) *Entry
- func (logger *Logger) WithField(key string, value interface{}) *Entry
- func (logger *Logger) WithFields(fields Fields) *Entry
- func (logger *Logger) WithTime(t time.Time) *Entry
- func (logger *Logger) Writer() *io.PipeWriter
- func (logger *Logger) WriterLevel(level stdLogger.Level) *io.PipeWriter
- type MutexWrap
- type StdFormatter
- type StdLogger
- type Termios
- type TextFormatter
Examples ¶
Constants ¶
const ( LabelCaller = "caller" LabelData = "data" LabelHost = "host" LabelLevel = "level" LabelMsg = "msg" LabelTime = "time" LabelTrace = "trace" )
Default key names for the default fields
const ( // PanicLevel level, highest level of severity. Logs and then calls panic with the // message passed to Debug, Info, ... PanicLevel = stdLogger.Panic // FatalLevel level. Logs and then calls `os.Exit(1)`. It will exit even if the // logging level is set to Panic. FatalLevel = stdLogger.Fatal // ErrorLevel level. Logs. Used for errors that should definitely be noted. // Commonly used for hooks to send errors to an error tracking service. ErrorLevel = stdLogger.Error // WarnLevel level. Non-critical entries that deserve eyes. WarnLevel = stdLogger.Warn // InfoLevel level. General operational entries about what's going on inside the // application. InfoLevel = stdLogger.Info // DebugLevel level. Usually only enabled when debugging. Very verbose logging. DebugLevel = stdLogger.Debug )
These are the standard logging levels. You can set the logging level to log on your instance of logger, obtained with `New()`.
const RFC3339Milli = "2006-01-02T15:04:05.000Z07:00"
RFC3339Milli defines an RFC3339 date format with miliseconds
Variables ¶
var ( // DEFAULTColor is the default TTY 'level' color. DEFAULTColor = "\033[38;5;46m" // ERRORColor is the TTY 'level' color for error messages. ERRORColor = "\033[38;5;208m" // FATALColor is the TTY 'level' color for fatal messages. FATALColor = "\033[38;5;124m" // PANICColor is the TTY 'level' color for panic messages. PANICColor = "\033[38;5;196m" // WARNColor is the TTY 'level' color for warning messages. WARNColor = "\033[38;5;226m" // DEBUGColor is the TTY 'level' color for debug messages. DEBUGColor = "\033[38;5;245m" // CallerColor is the TTY caller color. CallerColor = "\033[38;5;244m" // DataLabelColor is the TTY data label color. DataLabelColor = "\033[38;5;111m" // DataValueColor is the TTY data value color. DataValueColor = "\033[38;5;180m" // HostnameColor is the TTY hostname color. HostnameColor = "\033[38;5;39m" // TraceColor is the TTY trace color. TraceColor = "\033[38;5;244m" // TimestampColor is the TTY timestamp color. TimestampColor = "\033[38;5;72m" // ResetColor resets the TTY color scheme to it's default. ResetColor = "\033[0m" )
var AllLevels = []stdLogger.Level{ stdLogger.Panic, stdLogger.Fatal, stdLogger.Error, stdLogger.Warn, stdLogger.Info, }
AllLevels is a constant exposing all logging levels.
var ErrorKey = "error"
ErrorKey defines the key when adding errors using WithError.
Functions ¶
func Debug ¶
func Debug(args ...interface{})
Debug logs a message at level Debug on the standard logger.
func Debugf ¶
func Debugf(format string, args ...interface{})
Debugf logs a message at level Debug on the standard logger.
func Debugln ¶
func Debugln(args ...interface{})
Debugln logs a message at level Debug on the standard logger.
func Error ¶
func Error(args ...interface{})
Error logs a message at level Error on the standard logger.
func Errorf ¶
func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{})
Errorf logs a message at level Error on the standard logger.
func Errorln ¶
func Errorln(args ...interface{})
Errorln logs a message at level Error on the standard logger.
func Exit ¶
func Exit(code int)
Exit runs all the exit handlers and then terminates the program using os.Exit(code)
func Fatal ¶
func Fatal(args ...interface{})
Fatal logs a message at level Fatal on the standard logger then the process will exit with status set to 1.
func Fatalf ¶
func Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{})
Fatalf logs a message at level Fatal on the standard logger then the process will exit with status set to 1.
func Fatalln ¶
func Fatalln(args ...interface{})
Fatalln logs a message at level Fatal on the standard logger then the process will exit with status set to 1.
func Info ¶
func Info(args ...interface{})
Info logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func Infof ¶
func Infof(format string, args ...interface{})
Infof logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func Infoln ¶
func Infoln(args ...interface{})
Infoln logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func LevelString ¶ added in v0.1.19
LevelString convert the Level to a human readable string. E.g. PanicLevel becomes "panic".
func Panic ¶
func Panic(args ...interface{})
Panic logs a message at level Panic on the standard logger.
func Panicf ¶
func Panicf(format string, args ...interface{})
Panicf logs a message at level Panic on the standard logger.
func Panicln ¶
func Panicln(args ...interface{})
Panicln logs a message at level Panic on the standard logger.
func ParseLevel ¶
ParseLevel takes a string level and returns the log level constant.
func Print ¶
func Print(args ...interface{})
Print logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func Printf ¶
func Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
Printf logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func Println ¶
func Println(args ...interface{})
Println logs a message at level Info on the standard logger.
func RegisterExitHandler ¶
func RegisterExitHandler(handler func())
RegisterExitHandler adds an Exit handler, call log.Exit to invoke all handlers. The handlers will also be invoked when any Fatal log entry is made.
This method is useful when a caller wishes to log a fatal message but also needs to gracefully shutdown. An example usecase could be closing database connections, or sending a alert that the application is closing.
func SetCallerLevel ¶ added in v0.1.14
func SetCallerLevel(level int)
SetCallerLevel will adjust the relative caller level in log output.
func SetFormatter ¶
func SetFormatter(formatter Formatter)
SetFormatter sets the standard logger formatter.
func Warn ¶
func Warn(args ...interface{})
Warn logs a message at level Warn on the standard logger.
func Warnf ¶
func Warnf(format string, args ...interface{})
Warnf logs a message at level Warn on the standard logger.
func Warning ¶
func Warning(args ...interface{})
Warning logs a message at level Warn on the standard logger.
func Warningf ¶
func Warningf(format string, args ...interface{})
Warningf logs a message at level Warn on the standard logger.
Types ¶
type Entry ¶
type Entry struct {
Logger *Logger
// Contains all the fields set by the user.
Data Fields
// Time at which the log entry was created
Time time.Time
// Level the log entry was logged at: Debug, Info, Warn, Error, Fatal or Panic
// This field will be set on entry firing and the value will be equal to the one in Logger struct field.
Level logger.Level
// Message passed to Debug, Info, Warn, Error, Fatal or Panic
Message string
// When formatter is called in entry.log(), an Buffer may be set to entry
Buffer *bytes.Buffer
}
Entry is the final or intermediate logging entry. It contains all the fields passed with WithField{,s}. It's finally logged when Debug, Info, Warn, Error, Fatal or Panic is called on it. These objects can be reused and passed around as much as you wish to avoid field duplication.
func WithError ¶
WithError creates an entry from the standard logger and adds an error to it, using the value defined in ErrorKey as key.
func WithField ¶
WithField creates an entry from the standard logger and adds a field to it. If you want multiple fields, use `WithFields`.
Note that it doesn't log until you call Debug, Print, Info, Warn, Fatal or Panic on the Entry it returns.
func WithFields ¶
WithFields creates an entry from the standard logger and adds multiple fields to it. This is simply a helper for `WithField`, invoking it once for each field.
Note that it doesn't log until you call Debug, Print, Info, Warn, Fatal or Panic on the Entry it returns.
func WithTime ¶
WithTime creats an entry from the standard logger and overrides the time of logs generated with it.
Note that it doesn't log until you call Debug, Print, Info, Warn, Fatal or Panic on the Entry it returns.
func (*Entry) Debug ¶
func (entry *Entry) Debug(args ...interface{})
Debug logs a debug-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Debugln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Debugln(args ...interface{})
Debugln logs a debug-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Error ¶
func (entry *Entry) Error(args ...interface{})
Error logs a error-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Errorln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Errorln(args ...interface{})
Errorln logs a error-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Fatal ¶
func (entry *Entry) Fatal(args ...interface{})
Fatal logs a fatal-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Fatalln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Fatalln(args ...interface{})
Fatalln logs a fatal-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Info ¶
func (entry *Entry) Info(args ...interface{})
Info logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Infoln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Infoln(args ...interface{})
Infoln logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Panic ¶
func (entry *Entry) Panic(args ...interface{})
Panic logs a panic-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Panicln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Panicln(args ...interface{})
Panicln logs a panic-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Print ¶
func (entry *Entry) Print(args ...interface{})
Print logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Println ¶
func (entry *Entry) Println(args ...interface{})
Println logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) String ¶
String returns the string representation from the reader and ultimately the formatter.
func (*Entry) Warn ¶
func (entry *Entry) Warn(args ...interface{})
Warn logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Warning ¶
func (entry *Entry) Warning(args ...interface{})
Warning logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Warningln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Warningln(args ...interface{})
Warningln logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) Warnln ¶
func (entry *Entry) Warnln(args ...interface{})
Warnln logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Entry) WithError ¶
WithError add an error as single field (using the key defined in ErrorKey) to the Entry.
func (*Entry) WithFields ¶
WithFields adds a map of fields to the Entry.
func (*Entry) Writer ¶
func (entry *Entry) Writer() *io.PipeWriter
Writer returns an info-level log writer.
func (*Entry) WriterLevel ¶
func (entry *Entry) WriterLevel(level stdLogger.Level) *io.PipeWriter
WriterLevel returns a log writer with a specified leve.
type FieldLogger ¶
type FieldLogger interface {
WithField(key string, value interface{}) *Entry
WithFields(fields Fields) *Entry
WithError(err error) *Entry
Debugf(format string, args ...interface{})
Infof(format string, args ...interface{})
Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
Warnf(format string, args ...interface{})
Warningf(format string, args ...interface{})
Errorf(format string, args ...interface{})
Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{})
Panicf(format string, args ...interface{})
Debug(args ...interface{})
Info(args ...interface{})
Print(args ...interface{})
Warn(args ...interface{})
Warning(args ...interface{})
Error(args ...interface{})
Fatal(args ...interface{})
Panic(args ...interface{})
Debugln(args ...interface{})
Infoln(args ...interface{})
Println(args ...interface{})
Warnln(args ...interface{})
Warningln(args ...interface{})
Errorln(args ...interface{})
Fatalln(args ...interface{})
Panicln(args ...interface{})
}
The FieldLogger interface generalizes the Entry and Logger types
type FieldMap ¶
type FieldMap map[FieldLabel]string
FieldMap allows customization of the key names for default fields.
type Formatter ¶
The Formatter interface is used to implement a custom Formatter. It takes an `Entry`. It exposes all the fields, including the default ones:
* `entry.Data["msg"]`. The message passed from Info, Warn, Error .. * `entry.Data["time"]`. The timestamp. * `entry.Data["level"]. The level the entry was logged at.
Any additional fields added with `WithField` or `WithFields` are also in `entry.Data`. Format is expected to return an array of bytes which are then logged to `logger.Out`.
type Hook ¶
Hook defines a hook to be fired when logging on the logging levels returned from `Levels()` on your implementation of the interface. Note that this is not fired in a goroutine or a channel with workers, you should handle such functionality yourself if your call is non-blocking and you don't wish for the logging calls for levels returned from `Levels()` to block.
type JSONFormatter ¶
type JSONFormatter struct {
// DataKey allows users to put all the log entry parameters into a
// nested dictionary at a given key.
DataKey string
// DisableCaller disables caller data output.
DisableCaller bool
// DisableHostname disables hostname output.
DisableHostname bool
// DisableLevel disables level output.
DisableLevel bool
// DisableMessage disables message output.
DisableMessage bool
// DisableTimestamp disables timestamp output.
DisableTimestamp bool
// DisableTTY disables TTY formatted output.
DisableTTY bool
// Enable full backtrace output.
EnableTrace bool
// EscapeHTML is a flag that notes whether HTML characters should be
// escaped.
EscapeHTML bool
// ForceTTY forces TTY formatted output.
ForceTTY bool
// FieldMap allows users to customize the names of keys for default
// fields.
//
// For example:
// formatter := &TextFormatter{FieldMap: FieldMap{
// LabelCaller: "@caller",
// LabelData: "@data",
// LabelHost: "@hostname",
// LabelLevel: "@loglevel",
// LabelMsg: "@message",
// LabelTime: "@timestamp",
// }}
FieldMap FieldMap
// TimestampFormat allows a custom timestamp format to be used.
TimestampFormat string
sync.Once
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
JSONFormatter formats logs into parsable json.
type LevelHooks ¶
LevelHooks is an internal type for storing the hooks on a logger instance.
func (LevelHooks) Add ¶
func (hooks LevelHooks) Add(hook Hook)
Add a hook to an instance of logger. This is called with `log.Hooks.Add(new(MyHook))` where `MyHook` implements the `Hook` interface.
type Logger ¶
type Logger struct {
// The logs are `io.Copy`'d to this in a mutex. It's common to set this to a
// file, or leave it default which is `os.Stderr`. You can also set this to
// something more adventurous, such as logging to Kafka.
Out io.Writer
// Hooks for the logger instance. These allow firing events based on logging
// levels and log entries. For example, to send errors to an error tracking
// service, log to StatsD or dump the core on fatal errors.
Hooks LevelHooks
// All log entries pass through the formatter before logged to Out. The
// included formatters are `TextFormatter` and `JSONFormatter` for which
// TextFormatter is the default. In development (when a TTY is attached) it
// logs with colors, but to a file it wouldn't. You can easily implement your
// own that implements the `Formatter` interface, see the `README` or included
// formatters for examples.
Formatter Formatter
// The logging level the logger should log at. This is typically (and defaults
// to) `log.Info`, which allows Info(), Warn(), Error() and Fatal() to be
// logged.
Level stdLogger.Level
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Logger defines properties for managing logs and implements the std.Logger interface.
func New ¶
func New() *Logger
New creates a new logger. Configuration should be set by changing `Formatter`, `Out` and `Hooks` directly on the default logger instance. You can also just instantiate your own:
var log = &Logger{
Out: os.Stderr,
Formatter: new(JSONFormatter),
Hooks: make(LevelHooks),
Level: log.DebugLevel,
}
It's recommended to make this a global instance called `log`.
func (*Logger) Debug ¶
func (logger *Logger) Debug(args ...interface{})
Debug logs a debug-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Debugln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Debugln(args ...interface{})
Debugln logs a debug-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Error ¶
func (logger *Logger) Error(args ...interface{})
Error logs a error-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Errorln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Errorln(args ...interface{})
Errorln logs a error-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Fatal ¶
func (logger *Logger) Fatal(args ...interface{})
Fatal logs a fatal-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Fatalln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Fatalln(args ...interface{})
Fatalln logs a fatal-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Info ¶
func (logger *Logger) Info(args ...interface{})
Info logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Infoln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Infoln(args ...interface{})
Infoln logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Panic ¶
func (logger *Logger) Panic(args ...interface{})
Panic logs a panic-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Panicln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Panicln(args ...interface{})
Panicln logs a panic-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Print ¶
func (logger *Logger) Print(args ...interface{})
Print logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Println ¶
func (logger *Logger) Println(args ...interface{})
Println logs a info-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) SetNoLock ¶
func (logger *Logger) SetNoLock()
SetNoLock disables locking. When file is opened with appending mode, it's safe to write concurrently to a file (within 4k message on Linux). In these cases user can choose to disable the lock.
func (*Logger) Warn ¶
func (logger *Logger) Warn(args ...interface{})
Warn logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Warning ¶
func (logger *Logger) Warning(args ...interface{})
Warning logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Warningln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Warningln(args ...interface{})
Warningln logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) Warnln ¶
func (logger *Logger) Warnln(args ...interface{})
Warnln logs a warn-level message using Println.
func (*Logger) WithError ¶
WithError adds an error as single field to the log entry. All it does is call `WithError` for the given `error`.
func (*Logger) WithField ¶
WithField adds a field to the log entry, note that it doesn't log until you call Debug, Print, Info, Warn, Error, Fatal or Panic. It only creates a log entry. If you want multiple fields, use `WithFields`.
func (*Logger) WithFields ¶
WithFields adds a struct of fields to the log entry. All it does is call `WithField` for each `Field`.
func (*Logger) Writer ¶
func (logger *Logger) Writer() *io.PipeWriter
Writer returns an info-level log writer.
func (*Logger) WriterLevel ¶
func (logger *Logger) WriterLevel(level stdLogger.Level) *io.PipeWriter
WriterLevel returns a log writer with a specified leve.
type MutexWrap ¶
type MutexWrap struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
MutexWrap contains the mutex lock.
type StdFormatter ¶ added in v0.1.10
type StdFormatter struct {
// DataKey allows users to put all the log entry parameters into a
// nested dictionary at a given key.
DataKey string
// DisableCaller disables caller data output.
DisableCaller bool
// DisableHostname disables hostname output.
DisableHostname bool
// DisableLevel disables level output.
DisableLevel bool
// DisableMessage disables message output.
DisableMessage bool
// DisableTimestamp disables timestamp output.
DisableTimestamp bool
// Enable full backtrace output.
EnableTrace bool
// EscapeHTML is a flag that notes whether HTML characters should be
// escaped.
EscapeHTML bool
// FieldMap allows users to customize the names of keys for default
// fields.
//
// For example:
// formatter := &StdFormatter{FieldMap: FieldMap{
// LabelCaller: "@caller",
// LabelData: "@data",
// LabelHost: "@hostname",
// LabelLevel: "@loglevel",
// LabelMsg: "@message",
// LabelTime: "@timestamp",
// }}
FieldMap FieldMap
// TimestampFormat allows a custom timestamp format to be used.
TimestampFormat string
}
StdFormatter formats logs into text.
type StdLogger ¶
type StdLogger interface {
Print(...interface{})
Printf(string, ...interface{})
Println(...interface{})
Fatal(...interface{})
Fatalf(string, ...interface{})
Fatalln(...interface{})
Panic(...interface{})
Panicf(string, ...interface{})
Panicln(...interface{})
}
StdLogger is what your bdlm/log-enabled library should take, that way it'll accept a stdlib logger and a bdlm/log logger. There's no standard interface, this is the closest we get, unfortunately.
type TextFormatter ¶
type TextFormatter struct {
// DataKey allows users to put all the log entry parameters into a
// nested dictionary at a given key.
DataKey string
// DisableCaller disables caller data output.
DisableCaller bool
// DisableHostname disables hostname output.
DisableHostname bool
// DisableLevel disables level output.
DisableLevel bool
// DisableMessage disables message output.
DisableMessage bool
// DisableTimestamp disables timestamp output.
DisableTimestamp bool
// DisableTTY disables TTY formatted output.
DisableTTY bool
// Enable full backtrace output.
EnableTrace bool
// EscapeHTML is a flag that notes whether HTML characters should be
// escaped.
EscapeHTML bool
// ForceTTY forces TTY formatted output.
ForceTTY bool
// FieldMap allows users to customize the names of keys for default
// fields.
//
// For example:
// formatter := &TextFormatter{FieldMap: FieldMap{
// LabelCaller: "@caller",
// LabelData: "@data",
// LabelHost: "@hostname",
// LabelLevel: "@loglevel",
// LabelMsg: "@message",
// LabelTime: "@timestamp",
// }}
FieldMap FieldMap
// TimestampFormat allows a custom timestamp format to be used.
TimestampFormat string
sync.Once
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
TextFormatter formats logs into text.
 Source Files
¶
Source Files
¶
 Directories
¶
Directories
¶
| Path | Synopsis |
|---|---|
|
hooks
|
|
|
Package interceptor provides gRPC interceptors for common middleware requirements.
|
Package interceptor provides gRPC interceptors for common middleware requirements. |
|
log
Package log contains interceptor/middleware helpers for logging.
|
Package log contains interceptor/middleware helpers for logging. |