< Previous
Next >
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,2],
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
Example 2:
Given nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being modified to 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
Clarification:
Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
Note that the input array is passed in by reference, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
Internally you can think of this:
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
[Array]
[Two Pointers]
Similar Questions
- Remove Element (Easy)
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II (Medium)
Hints
Hint 1
In this problem, the key point to focus on is the input array being sorted. As far as duplicate elements are concerned, what is their positioning in the array when the given array is sorted? Look at the image above for the answer. If we know the position of one of the elements, do we also know the positioning of all the duplicate elements?
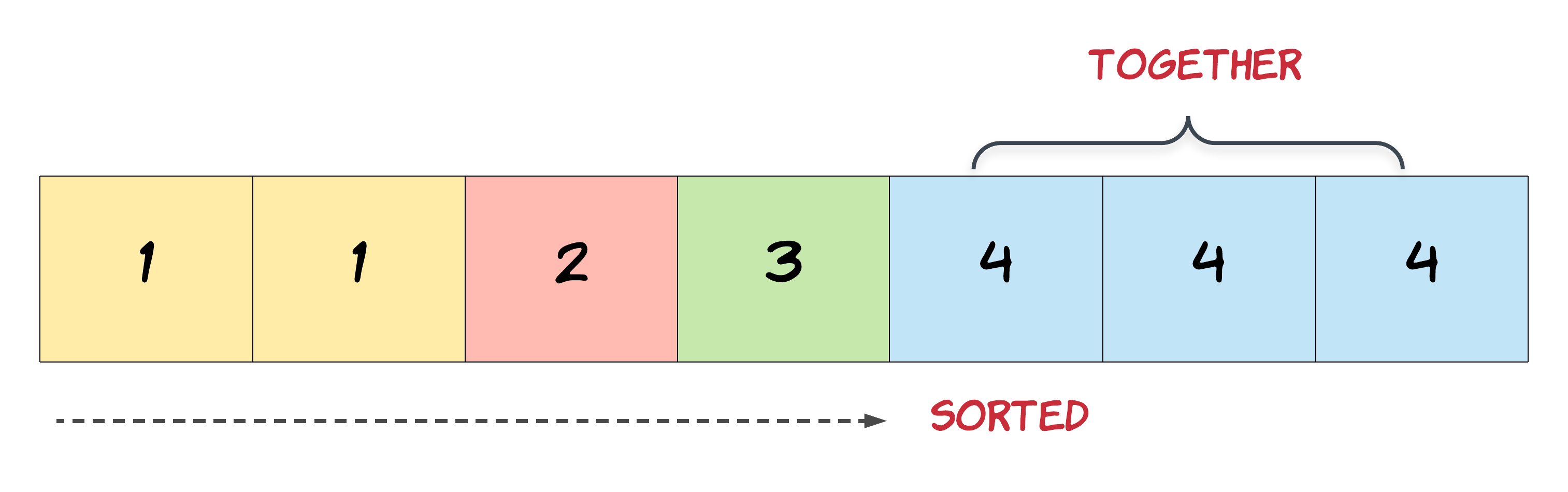
Hint 2
We need to modify the array in-place and the size of the final array would potentially be smaller than the size of the input array. So, we ought to use a two-pointer approach here. One, that would keep track of the current element in the original array and another one for just the unique elements.
Hint 3
Essentially, once an element is encountered, you simply need to bypass its duplicates and move on to the next unique element.
 Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶